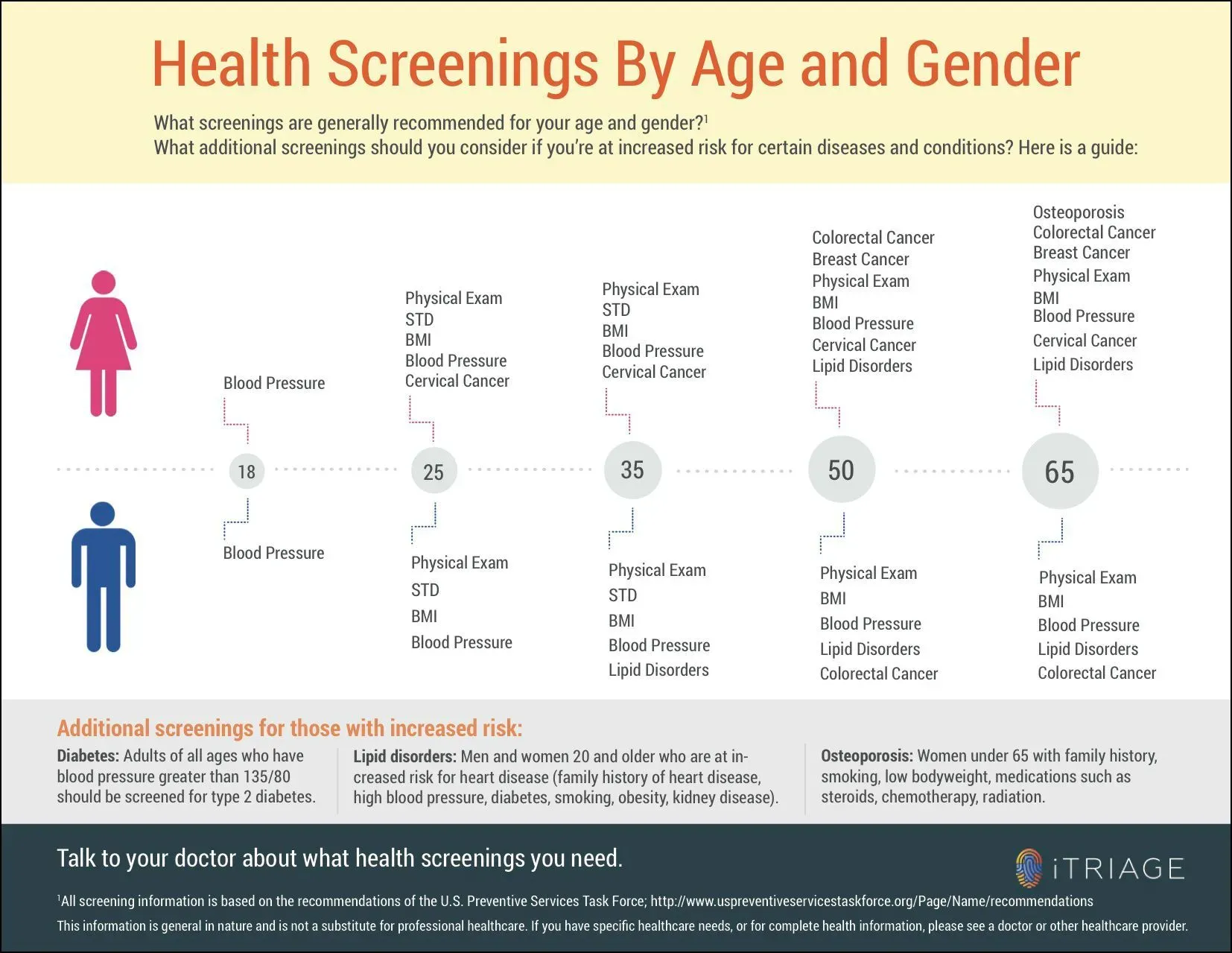
Preventive health screenings are a cornerstone of modern health care and a reliable compass for staying well over time, guiding patients, families, and clinicians toward informed choices. They uncover hidden risks before symptoms show, helping people avoid serious illness and supporting timely treatment decisions that can reduce complications and preserve long-term quality of life for patients and providers to set realistic goals together. When people imagine staying well, they often picture diets, workouts, or vitamins, yet the steady practice of regular checks remains the quiet engine behind preventive care today. By prioritizing screenings, you can reduce hospitalizations, tailor interventions to your unique risk profile, empower more timely conversations with your clinician, and build a collaborative plan that evolves with your health. This article explains what screenings are typically recommended, how evidence-based practices shape a personal plan, and practical steps to stay engaged, informed, and on track toward a healthier tomorrow.
Viewed from another angle, health maintenance can be framed as a series of wellness checks woven into routine care. These measures rely on evidence-informed screening strategies and personalized risk assessments to determine what tests are appropriate and when to schedule them. The emphasis shifts from one-time testing to ongoing monitoring, empowering patients to recognize signals, discuss options with clinicians, and adjust plans as life circumstances change. Advances in digital health, wearables, and telemedicine support this approach by making follow-ups smoother and enabling timely action when needed. By integrating these practices, individuals can build resilience, avoid gaps in care, and stay motivated to keep preventive routines aligned with personal goals.
Preventive Health Screenings: The Cornerstone of Early Disease Detection
Preventive health screenings are the cornerstone of modern medical care, enabling early disease detection and guiding timely action before symptoms appear. When you view preventive health screenings as part of a proactive routine, you gain clarity about what tests to expect and why they matter, all while following established screening guidelines. This approach integrates with routine health checks to create a continuous, informed picture of your well-being.
By prioritizing screenings, you empower yourself to reduce the risk of serious illness, lower hospitalizations, and extend healthy years. The results from preventive health screenings help tailor lifestyle changes, preventive medications, or referrals to specialists, turning wellness checks into practical steps for sustaining vitality. In this light, preventive health screenings are not merely diagnostic tools but a proactive partnership with your body and your healthcare team.
Integrating Screening Guidelines with Routine Health Checks and Wellness Checks Across Life Stages
To make preventive care work for you, follow screening guidelines that consider age, sex, family history, and other risk factors. Think in terms of routine health checks you can schedule regularly, ensuring cancer screenings, cardiovascular risk assessments, and metabolic tests align with your current life stage. This life-course approach helps you stay ahead of potential issues and keeps wellness checks meaningful and actionable.
Practical steps include building a calendar with your clinician, understanding what tests mean, and leveraging technology to stay on track. Address barriers such as cost or access by exploring low-cost options, telehealth follow-ups, and community screening programs. By integrating wellness checks with routine health checks and adhering to screening guidelines, you can maintain momentum toward healthier daily habits and more informed, timely decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are preventive health screenings and why are routine health checks important for early disease detection?
Preventive health screenings are medical tests, assessments, and physical checks designed to identify health risks in people who feel well. They include routine health checks such as blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes screening (HbA1c), cancer screenings, and vision/hearing tests. By enabling early disease detection, these screenings help prompt timely treatment, reduce complications, and can lower long-term costs. Work with your clinician to tailor a plan based on your age, family history, and personal risk factors.
How can I align my preventive health screenings with official screening guidelines and wellness checks?
To align with screening guidelines, discuss your age, sex, family history, and risk factors with your clinician. Official screening guidelines from organizations like USPSTF provide recommended tests and intervals, but your plan should be personalized. Create a practical schedule that combines preventive health screenings with regular wellness checks, set reminders, and update it as your health changes. Typical focus areas include blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose screening, cancer screenings where indicated, and appropriate immunizations.
| Aspect | Key Points | Notes / Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| What are preventive health screenings and why they matter |
|
Foundational for early intervention and proactive healthcare relationships. | |
| How screenings save lives |
|
Leads to better outcomes and cost savings across individuals and communities. | |
| Core screenings and how they fit into your life |
|
Integrates routine checks with risk-based testing to tailor a plan. | |
| Aligning with guidelines and tailoring |
|
Encourages personalized screening schedules. | |
| Screening by age and risk: overview |
|
Provides practical, stage-based planning for ongoing preventive care. | |
| Preparing for your screenings: practical steps |
|
Enhances accuracy and reduces anxiety; supports ongoing monitoring. | |
| Barriers to preventive screenings and how to overcome them |
|
Offers actionable strategies to improve access and participation. | |
| Interpreting results and next steps |
|
Emphasizes timely action and clear communication with providers. | |
| Lifestyle and preventive health: reducing risk beyond screenings |
|
Connects daily choices with long-term health outcomes. | |
| Technology and future trends in preventive care |
|
Shows how innovation can optimize when and what tests are needed. |
Summary
Preventive health screenings provide a clear map for safeguarding long-term health. This descriptive overview highlights how routine tests detect risks early, guide personalized care, and inspire healthier daily choices. By aligning with evidence-based guidelines, overcoming access barriers, and integrating screenings with regular wellness checks, individuals can reduce surprises, lower unnecessary interventions, and build resilience for years to come.