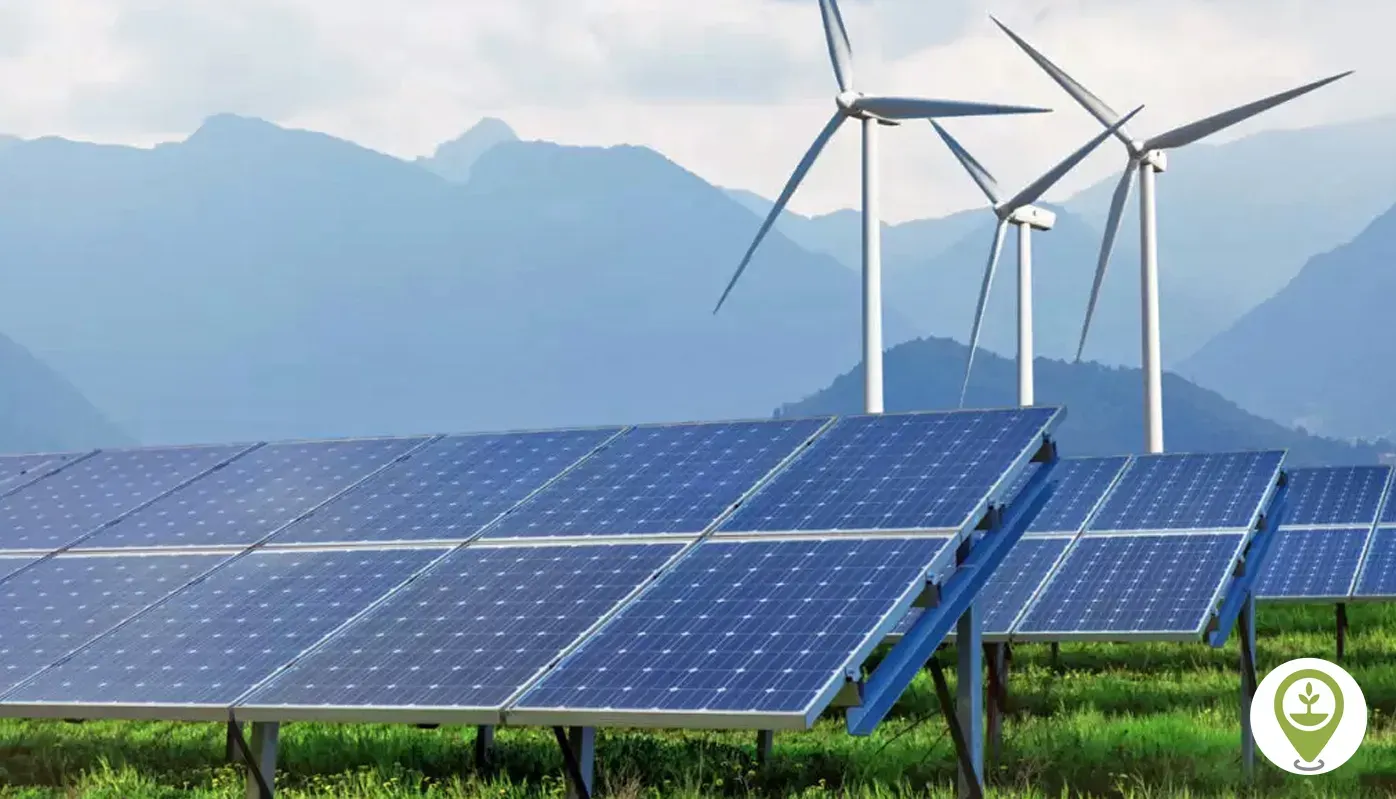
Clean energy sits at the center of modern economies, powering homes, businesses, and communities while shaping a healthier climate and brighter prospects. As costs fall and technology scales, renewable energy provides cleaner power, boosts resilience, and opens new opportunities for workers, families, and local industries. The path forward blends smarter grids, expanded storage, and rigorous energy efficiency to cut emissions while keeping power affordable and reliable. Smart investment, robust policy, and public-private collaboration align to lower bills, improve air quality, unlock local innovation, and strengthen energy security. This momentum signals a sustainable, inclusive energy future for people and places around the globe.
In other words, this topic can be framed through green power, low-emission electricity, and carbon-free generation rather than a single technology. A green power portfolio blends sun, wind, and other resources with storage, flexible transmission, and demand-side efficiency. Public and private investment accelerates the shift by signaling long-term policy, expanding grid capacity, and supporting affordable, climate-conscious choices. Communities benefit from cleaner air, greater energy security, and more stable prices as the broader energy system becomes more resilient. Businesses see opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and services that accompany the deployment of these eco-friendly energy solutions. Ultimately, the transition hinges on clear incentives, accessible financing, and inclusive planning that leaves no one behind.
Clean Energy at Home and Beyond: How Renewable Energy Powers Everyday Life
Clean energy is increasingly woven into daily life, from rooftop solar panels and heat pumps to energy‑efficient appliances. By tapping renewable energy sources such as sunlight, wind, and geothermal heat, households can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and shield themselves from fossil‑fuel price volatility. This shift aligns with climate solutions and the broader energy transition, delivering reliable power while lowering environmental impact.
Communities and small businesses stand to gain from local generation, lower electricity bills over time, and greater resilience during extreme weather events. As renewable energy shares rise, decarbonization accelerates and sustainable energy systems become more accessible, supporting local jobs in installation and maintenance and expanding opportunities for producers, installers, and service providers.
Grid Modernization for a Sustainable Energy Future: Storage, Policy, and Decarbonization
Modernizing the grid is essential to accommodate a diverse mix of renewable energy sources and to maintain reliability. Energy storage technologies—ranging from lithium‑ion batteries to emerging solid‑state and flow batteries—help balance supply and demand, smooth price swings, and keep lights on when solar and wind fluctuate. Coupled with smart management and demand response, storage is a cornerstone of the energy transition and key to delivering climate solutions at scale.
Sound policy and economics accelerate adoption by reducing investment risk and unlocking private capital for transmission, storage, and electrification of end‑use sectors. By combining renewables with energy efficiency and proactive workforce planning, governments and businesses can drive decarbonization across electricity, transportation, and industry, advancing a sustainable energy future while protecting affordability and ensuring a just transition for workers and communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is clean energy, and why is it central to the energy transition and decarbonization?
Clean energy means power generated from sources that do not deplete finite resources or emit harmful pollutants, with the most common examples being solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. It sits at the core of climate solutions and is central to the energy transition and decarbonization, helping to lower emissions, improve air quality, and strengthen energy security. As renewable energy costs fall and storage and grid improvements advance, clean energy also brings jobs, resilience, and long-term affordability to households and businesses.
How do renewable energy, storage, and grid modernization advance climate solutions and a sustainable energy future?
Renewable energy, storage, and grid modernization work together to deliver a reliable, affordable clean energy system and advance climate solutions. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind cut emissions, while storage (batteries and other technologies) smooths supply to match demand. Modernized grids—with smart meters, flexible tariffs, and demand response—improve resilience and enable faster deployment of the energy transition, benefiting households, businesses, and communities.
| Key Topic | Description | Why It Matters | Examples / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition of Clean Energy | Clean energy refers to energy generated from sources that do not deplete finite resources or cause harmful emissions. It replaces or reduces fossil fuels with renewables and technologies that minimize environmental impact, forming the central path to decarbonization. | Enables scalable decarbonization, improves air quality, and supports sustainable growth. | Renewables (solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, biomass); energy efficiency; storage; decarbonization pathways. |
| Everyday Benefits | Lower electricity costs over time, enhanced energy security, local job opportunities in manufacturing and installation, and cleaner air and healthier living conditions. | Reduces price spikes tied to fossil fuels; strengthens resilience and public health. | Distributed generation, on-site solar, energy efficiency programs. |
| Key Renewable Energy Sources | Solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass form a diversified portfolio that enhances reliability and reduces costs when combined. | Diverse sources lower risk from variability and enable smoother power delivery. | Rooftop solar, solar farms; onshore/offshore wind; hydro projects; geothermal heating; biomass with sustainable practices. |
| Grid Modernization & Storage | Modern grids, forecasting, flexible resources, and transmission upgrades; storage technologies (lithium-ion, solid-state, flow) balance supply and demand. | Ensures reliability, reduces price volatility, and maintains grid stability amid transition. | Smart meters, dynamic pricing, demand response; transmission upgrades; on-site storage; electrification. |
| Policy & Economics | Policy frameworks, targets, carbon pricing, and funding lower investment risk and accelerate deployment; renewables becoming cheaper; just transition to workers. | Attracts private capital, creates jobs, and supports broad adoption. | Green procurement, government-private investments, electrification of end-use sectors. |
| Real-World Impacts & Case Studies | Coastal cities blending offshore wind, solar, and batteries; manufacturing hubs with on-site solar; rural community solar and microgrids improve resilience and cut costs. | Demonstrates tangible benefits and scalability of renewables. | Offshore wind + solar; community solar; microgrids. |
Summary
Clean energy is not a single solution but a comprehensive pathway toward a sustainable future. Expanding renewables, upgrading grids, deploying storage, and enacting thoughtful policies can reduce emissions, strengthen energy security, and boost economic resilience. The transition offers tangible benefits for households, businesses, and nations—lower bills, cleaner air, more local jobs, and improved public health—while driving innovation and fair growth. Framed as an opportunity for equitable progress, the Clean energy transition invites collaboration across sectors to power a healthier planet and a thriving economy.