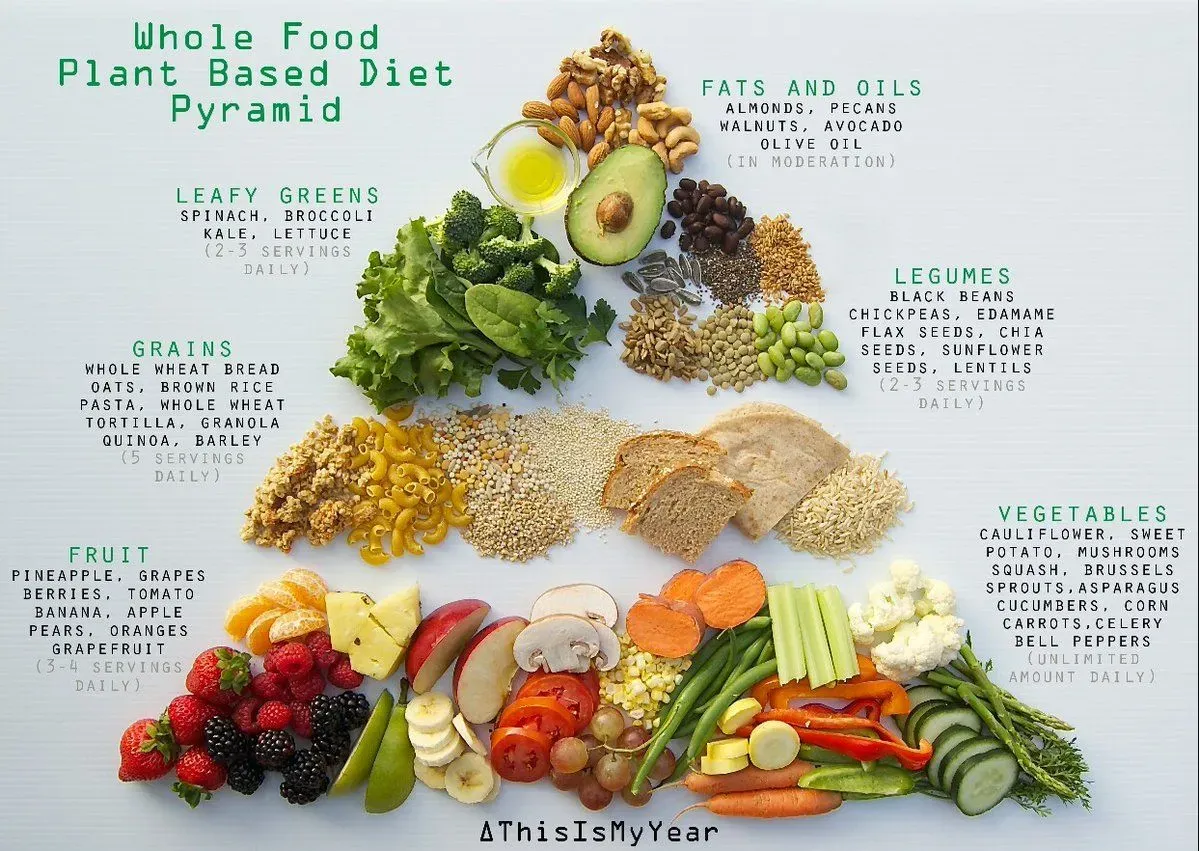
A plant-based diet for health can reshape how you think about meals, energy, and well-being. With growing evidence, adopting more plant-based meals is linked to better heart health, weight management, and steadier blood sugar. This guide highlights the benefits of a plant-based diet and offers practical plant-based tips to help you start small, stay consistent, and savor nutrient-dense choices. You’ll discover a variety of vegetarian diet health benefits framed around real-life meals, so you can enjoy flavor without sacrificing nutrition. From breakfast to dinner and snacks, practical plant-based meal ideas that showcase diverse flavors make plant-forward eating doable, delicious, and sustainable.
Beyond the headline term, you may hear plant-forward eating described as a veggie-forward lifestyle, a flexitarian pattern, or simply meatless meals—all aiming to put vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds at the center. This approach aligns with Latent Semantic Indexing principles by connecting concepts like fiber-rich diets, micronutrient density, antioxidant phytonutrients, and sustainable protein sources to heart health and energy. By emphasizing variety and balance, you can achieve cardiovascular benefits, stable energy, and digestive wellness without feeling restricted. Practical choices—plant-based meal ideas such as bean bowls, tofu stir-fries, lentil soups, and quinoa salads—illustrate how to live a health-supportive, plant-forward lifestyle.
Plant-based diet for health: Practical strategies for energy, vitality, and long-term wellness
A plant-based diet for health invites you to reframe meals around vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. It’s not about perfection, but consistency, variety, and choosing nutrient-dense options most of the time. The benefits of a plant-based diet are supported by research and translate to real-life improvements in heart health, weight management, blood sugar stability, and daily energy. By prioritizing plant-based meals, you naturally boost fiber, phytonutrients, vitamins, and minerals while reducing ultra-processed foods and added sugars.
To make this shift sustainable, lean on practical plant-based tips: start with one plant-based meal per day and gradually expand, build meals around a half-plate of vegetables plus a protein and a whole grain, and batch-cook staples like beans, lentils, and grains. Ensure nutrient adequacy by including diverse protein sources, strategies to enhance iron and calcium absorption, and consideration of vitamin B12, iodine, omega-3s, and vitamin D as needed. These considerations align with the vegetarian diet health benefits observed in varied populations and help you sustain long-term health without sacrificing flavor or satisfaction.
As you experiment, you’ll discover that plant-based meal ideas—from colorful bowls to globally inspired dishes—offer energy-dense, satisfying options that support daily vitality. This approach shows that the benefits of a plant-based diet extend beyond individual nutrients to overall patterns of eating that promote ongoing wellness and performance.
Creative plant-based meal ideas for sustained health and performance
Creative plant-based meal ideas help keep health and performance top of mind by combining variety, flavor, and practicality. Rotating cuisines—Indian dals, Mediterranean bowls, Mexican-inspired bean tacos, and Asian stir-fries—ensures a broad spectrum of micronutrients and phytochemicals while keeping meals exciting. Emphasizing plant-based meals and smart substitutions makes it easier to enjoy the vegetarian diet health benefits over time and to experience the broader benefits of a plant-based diet.
A sample day can illustrate the approach: breakfast could be overnight oats with chia seeds and berries; lunch a lentil or chickpea bowl with colorful vegetables and tahini dressing; dinner a tofu or tempeh stir-fry with brown rice and a rainbow of vegetables; snacks like hummus with veggie sticks or fruit with nuts. By focusing on plant-based meal ideas that pair fiber, protein, and healthy fats, you sustain steady energy and faster recovery—key advantages highlighted in the overall benefits of a plant-based diet.
To make these meals practical, use a simple plan and prep routine: batch-cook beans and grains, roast a tray of vegetables, and keep a rotating repertoire of sauces and spices. Track progress by energy, digestion, mood, and performance rather than calories alone, and keep reminding yourself that plant-based tips—such as balancing portions, choosing minimally processed ingredients, and incorporating foods rich in iron, calcium, and omega-3s—support long-term adherence and enjoyment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of a plant-based diet for health?
A plant-based diet for health emphasizes vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and minimally processed foods. When well planned, it supports heart health, helps with weight management, improves insulin sensitivity, and boosts energy and gut health. Key nutrients to focus on include protein variety, iron, calcium, vitamin B12, iodine, omega-3s, and ample fiber. Remember: a flexitarian pattern or vegetarian meals most of the time can deliver meaningful health benefits without aiming for perfection.
What are easy plant-based meal ideas for health, and what plant-based tips can help me start?
Here are simple plant-based meal ideas for health to get you started: breakfast with overnight oats featuring chia, berries, and fortified plant milk; lunch with a chickpea salad wrap; dinner with a tofu stir-fry and vegetables served over brown rice; snacks like hummus with veggies. Plant-based tips to help you start include beginning with one plant-based meal per day, using the half-plate rule, batch-cooking staples like beans and grains, and rotating protein sources for variety. This approach aligns with the plant-based diet for health, prioritizing whole foods, fiber, and nutrient density while keeping meals enjoyable and sustainable.
| Topic | Key Points | Notes/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Definition and meaning | Emphasizes vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and minimally processed foods; prioritizes plant foods and reduces reliance on refined or highly processed items; gradual/flexible approach (flexitarian patterns allowed). | Focus on balance and nutrient adequacy; not always meat-free for everyone. |
| Why consider it | Potential benefits beyond nutrition: weight management, heart health, better blood sugar control, improved energy, gut health; rich in fiber and phytonutrients; supports long‑term health. | Well-planned approach can improve lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and energy levels. |
| Core foods | Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds; minimize highly processed meats, refined grains, added sugars. | Aim for variety and color; include protein, iron, calcium, B12, iodine, and omega-3 sources. |
| Key nutrients to focus on | Protein: beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu/tempeh, quinoa; Iron, Calcium; Vitamin B12 (supplements/fortified foods); Iodine and omega-3s; Vitamin D. | Note pairing strategies (e.g., iron with Vitamin C) to enhance absorption. |
| Practical tips to start and sustain | Start with one plant-based meal per day; use half-plate vegetables, quarter protein, quarter whole grains; prioritize whole foods; plan & batch-cook; diversify protein; smart shopping; track nutrients; use quick cooking methods; enjoy meals socially. | Adapt to your schedule; build a simple weekly plan. |
| Myths vs realities | Myths: inadequate protein, iron, calcium; dairy is essential; plant-based is expensive. Realities: adequate protein with legumes/soy; iron/calcium can be met with fortified foods and proper pairing; dairy alternatives exist; cost can be controlled with smart planning. | Pair grains with legumes; choose fortified options; budget-friendly staples like beans/oats/rice. |
| Meal ideas and day examples | Breakfast: overnight oats, smoothie bowls, avocado toast; Lunch: chickpea wrap, lentil soup, quinoa bowls; Dinner: tofu stir-fry, lentil dal, roasted chickpeas with veggies; Snacks: hummus with veggies, fruit with nuts. | Rotate flavors and cultural cuisines for variety. |
| Special considerations | Athletes: emphasize protein variety and timing; Families with kids: involve kids in prep; Medical conditions: consult professional guidance and consider supplements as needed. | Personalization matters; adjust for energy needs. |
| Sustainable plan | Flexible structure with identifiable go-to meals; include protein and whole grains; track progress through energy, mood, digestion and cravings instead of weight alone. | Start simple, then iterate as you learn what works for you. |